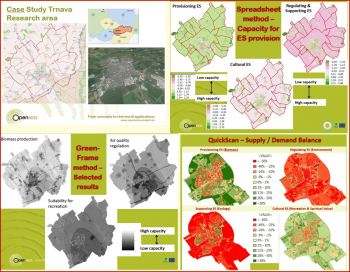
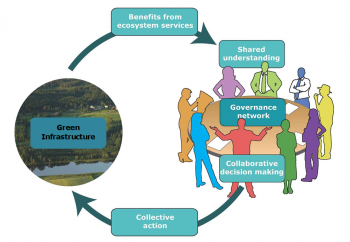
Socio-cultural valuation of green space in peri-urban Edinburgh
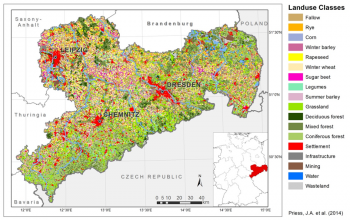
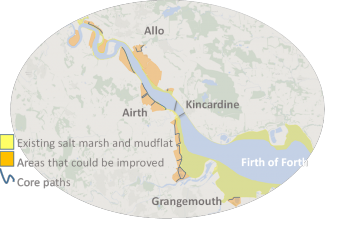
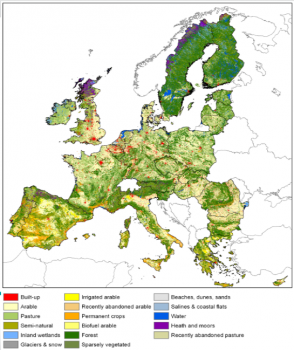
Place-based studies around peri-urban Edinburgh are working with policy makers to better understand society's socio-cultural values of green space. The exemplar aims to: Understand appreciation of ecosystem services in the Pentland Hills; Understand potential to offset urban development in East Lothian; Identify societal ecosystem services benefits in urban and peri-urban contexts; Assess the socio-cultural values of these ecosystem services; Apply, test and further develop ecosystem service valuation methods.