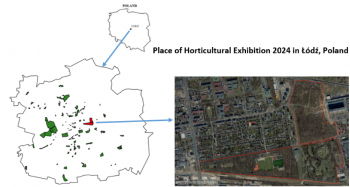
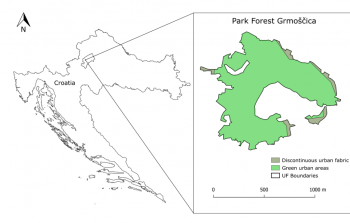
Green corridor in Passeig de Sant Joan, Barcelona (ENABLE project)
To improve public space functionality and use, to increase access to green spaces for district residents (Eixample), to contribute to higher biodiversity in the city, and to promote more and different retail activity at the ground floor of buildings, so to rejuvenate/boost the local economy.