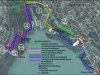
Scale of the project: neighbourhood
Scales impacts from this NbS action should be assessed: city, regional
Urban density in which the NbS is implemented: low (suburb at the limit with rural areas, etc.)
The area was problematic, because of sludge soil.
- Development of an ecological park at the lake Balaton
The plans of the municipality and the local civic organzation were to develop a pleasant, ecological park filled with different kind of leisure activities from the neglected gulf.
The objective is a comprehensive reconstruction of the area in Balatonfűzfő, from Fövenyfürdő Beach to Tobruki Beach is enabling the semi-natural utilization of the area near the city and near the lake. This project has two phases:
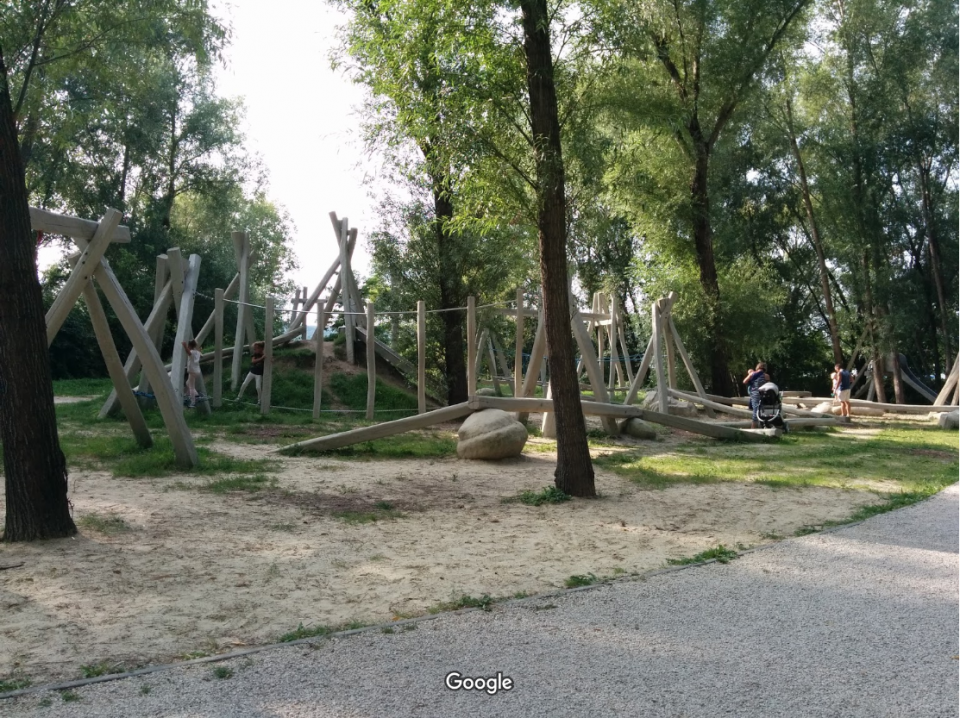
- The first phase a semi-natural promenade with special playground was created. The first phase also contained the development of an alternative route for the Balaton Bikering Road with catering facilities for bikers and tourists too. This means a much adventurous section for the bikers.
- The second phase of the project will connect the two beaches with a further promenade.
The NbS porject is also combined with another environmental friendly solution:
- Renewable energy system (solar panels, etc.)
- A new bridge was built with design fit harmoniously into their enviroment, made of eco-friendly materials
The project had dual purposes. On the one hand it gives the oppurtunity for recreation in natural environment for the citizens, especially families. They ensure active freetime facilities. The project area is easily accessible. Morover there is the new phase of the Balaton Bike Ringroad so the important beneficieries of the projekt are the bikers from the region, from the country or other sport tourists as well.
- Better protection and restoration of coastal ecosystems
- Restoring ecosystems and their functions
- Improve connectivity and functionality of green and blue infrastructures
- Increase Biodiversity
- Increase quality and quantity of green and blue infrastructures
- Improve air quality
- Improve water quality
- Increase accessibility to green open spaces
- Increase amount of green open spaces for residents
- Increase well-being
Process enablers:
Knowledge drivers → Awareness → NbS ambassadors
Governance drivers → cocreation and participation → Reflexive or adaptive governance
Economy drivers → Public private partnerships
Forward -thinking and sustainable plan, PPP finance, good partners
Process inhibitors:
Knowledge barriers → Accessibility to information → Information overload
Governance barriers → Institutional barriers → Lack of coordination
Economy barriers → Perception of the benefits → Appreciation of non-economic benefits
The project was a bit oversized compared to the size of the city. A serious collaboration was needed between the partners in question: the municipality, designers and the management of the sport clubs. Despite of the endurence of the stakeholders there were many problems during the development and implementation phase. The main issue was the uncleared ownership of the development site. The cooperation with the private sector wasn't without any failer too.
Legal constrains for the intervention: the construction area was underutilized and abandoned, according to the plans the full implementation has had severe financial difficulties: dealing with property owners, ensure the smooth communication between partners and the maintenance. Several partners have had to cooperate during the realization of the project. Thus these forwardthinking and sustainable plans was implemented in several stages. So far the first stage has been finished.
BUSINESS MODEL:
Business cluster: Technological
Business model: Substitute with renewables and natural processes
Business cluster: Social
Business model: Encourage sufficiency
The innovativeness of the business model is, that local private investors and the local sport clubs were both involved in the planning and implementation process. The co-operation of private and civil partners is a novelty in Hungarian project management.
Temporal perspective
Expected time for the NBSto become fully effective after its implementation: short (immediately to few months)
Feedback on the functioning of the project: The project has already been adapted to new requisites.
Due to the project two parts of the city has been interlinked to each other with a recreational area along the lakeside. Safe bikeway and a passage with full of joyful experiences has been created, adventurous both for families and adults. Several services serve the peaceful recreation of visitors: restaurants, sport facilities, playgrounds or services for bikes and other service units.
Expected life time of the intervention: around 10 years
Dates (for project delivered): project delivered but specific date unknow...
Careful planning process was necessary, financialized by the municipality. Further,
stakeholders had to be found in the region, like private firms and sport clubs to associate to the implementation.
Also, governmental agreement was fundamental as the bike road connects to the
regional bikering road network.
Global (estimated) cost of the project: 200k€- 1M€
Finance cluster: cluster1 public financing
Finance model: Cohesion Fund
90% of the costs was covered by EU funds, while the remaining 10% was financed by the local municipality, and other national funds. The installation of sport facilities was covered by private investiors, but the local sport clubs also take part in the operation.
- Objects shapes (1)
- On the ground (1)
- Parks and gardens
- Large urban public parks
- Objects shapes (2)
- On the ground (2)
- Choice of plants
- Diversity of plant species
Attila, Nóti (noti.attila@balatonfuzfo.hu)
Municipality or metropolitan service (www.balatonfuzfo.hu)
Nike street 1, Balatonfűzfő, 8184, Hungary
Further information
Nature4Cities (https://www.nature4cities.eu/) aims to develop a knowledge diffusion around Nature-Based Solution (NbS) and a decision support platform through new collaborative models.
This project is part of the Nature4Cities's pioneer case studies database, it will feed the observatory, NbS pre-selection and replication tools, gathered into the Geocluster4NBS.
This project was chosen as a pioneer case study for the following reasons: the area was problematic, because of the presence of sludge-soil. The development applied several NbS tools, as plant choice and habitat conservation. Due to the intervention an urban public park was developed. It was necessary to find those tools, that are appropriate to endure the loading of the foreseeable utilization and the exposure to diverse weather situations too.
Nature4Cities project has received funding from the European Union’s Horizon 2020 research and innovation program under grant agreement No 730468.