The project is built upon the strategic lines of the Mediterranean basin regions. To begin this process, NBS will be tested in 5 demonstration regions, using front-line scientific, technological, social, and business innovations as well as transformative solutions. Then, the most promising NBS will be transferred to 3 replicating regions.
Explore our research and materials at DRYAD Project Knowledge Center.
Project Objectives
DRYAD’s overarching aim is to support the EU Mission Adaptation to Climate Change by demonstrating, modelling, and enabling the uptake of climate-resilient Nature-based Solutions (NbS) for Mediterranean agro-silvo-pastoral ecosystems (MAEs).
The main objective of DRYAD is to demonstrate NbS for MAES, provide tools and implementation guidelines to promote sustainable and climate-resilient practices and facilitate regional adaptation planning.
The specific objectives include:
- Develop and test novel scientific tools and models to enhance MAE resilience.
- Demonstrate methodologies and management approaches in Pilot Demonstration Areas with Living Lab support.
- Scale successful pilot methodologies across broader Demonstration Regions.
- Improve reliability and dissemination of scientific and management methodologies, integrating high-TRL modelling into Living Labs.
- Facilitate co-creation and mutual learning through a Community of Practice approach.
- Increase multi-stakeholder awareness of NbS effectiveness to address ecological and socio-economic climate risks.
- Support regions and authorities in defining and deploying multi-level governance frameworks for integrated climate adaptation.
Methods
DRYAD’s methodology spans scientific, technological, social and governance dimensions, including:
- Field-based and Implementation Methods: Implementation of NbS in Pilot Demonstration Areas and then upscaling to 5 Demonstration Regions in Andalusia, Extremadura, Alentejo, Sardinia, and Aetoloakarnania.
- Living Lab frameworks for co-creation, co-implementation and co-validation with stakeholders.
- Monitoring and Data Acquisition: Real-time and cost-effective environmental monitoring combining in situ sensors (LoRaWAN) and remote sensing data.
- Web-based geospatial data management system (GDMS) for organizing spatial and temporal field and RS data.
- Integrated ecohydrological models (e.g., coupling SCOPE, STEMMUS, MODFLOW6) to represent interactions between drought, soil-plant-water systems and to assess NbS impacts.
- Decision Support System (DSS) embedded in GDMS with tools for stakeholders and regional planners.
- Upscaling and Knowledge Transfer
- Community of Practice and multi-stakeholder engagement for shared learning and broader uptake and replication of NbS in 3 Replication Regions
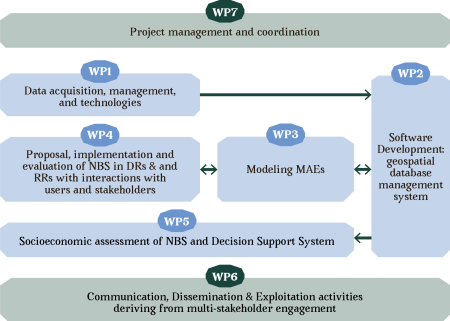
- Dissemination - It is structured in 7 interrelated Work Packages, 5 technical work packages (1, 2, 3, 4 and 5) will be related to the 2 transversal ones (6 and 7).
Barriers
- Increasing climate pressures (droughts, heatwaves, water scarcity and land degradation) that reduce the resilience of Mediterranean agro-silvo-pastoral ecosystems.
- Fragmented and insufficient monitoring and data integration, limiting the ability to assess ecosystem responses and NbS performance across scales.
- Limited availability of integrated modelling and decision-support tools capable of capturing coupled eco-hydrological and socio-ecological processes.
- Governance and institutional complexity, including weak coordination across administrative levels and sectors involved in land and water management.
- Low uptake and scalability of Nature-based Solutions, due to stakeholder awareness gaps, uncertainty on costs and benefits, and context-specific constraints.
Funding
Grant agreement ID: 101156076











